Week 3: In-Class#
Coding Practice#
Code 3.1: Blood Pressure#
Measurement of blood pressure consists of two values: systolic blood pressure (a higher value) and diastolic blood pressure (a lower value). Based on these two values, blood pressure can be categorized as indicated in the chart below.
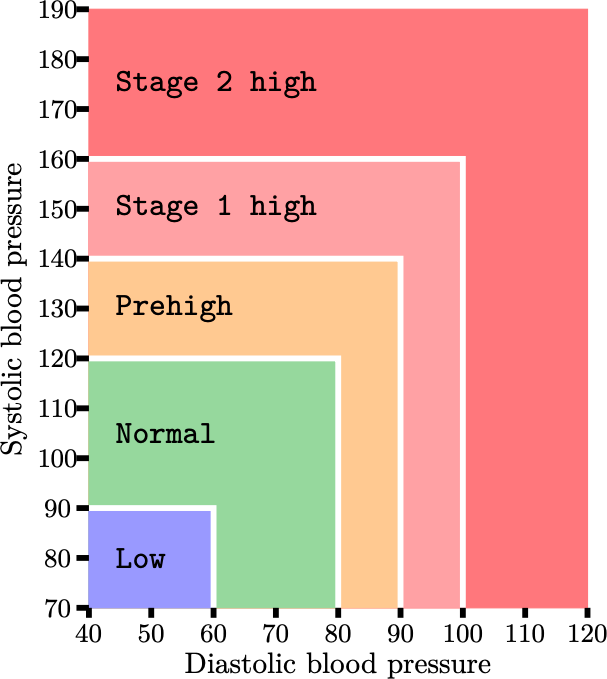
Your task is to categorize blood pressure based on systolic and diastolic values. If a measurement is between categories, it should be categorized as belonging to a higher (more severe) category.
For example, if the systolic blood pressure is 120 and the diastolic blood pressure is 65, according to the chart, the measurement is between the normal and prehigh blood pressure categories, so it should be categorized as prehigh.
Pen & Paper
It is normal to write a measurement of blood pressure as two numbers separated by a slash, for example, 120/65, and read it as “120 over 65”.
Consider following cases, and determine the blood pressure category for each case based on the chart above: 100/95, 80/50, 110/70, 133/82, 141/99, 189/101, 90/60, 170/80, 140/50, 160/60.
Demo
Write a script which relies on the numeric variables with systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure, given in variables systolic and diastolic. The code should assign a string variable with the blood pressure category, as in the chart above. If a measure is between categories, a higher value should be used. The code should also print the blood pressure category. Test your code with all the cases from the Pen & Paper exercise.
Code 3.2: Summer Days#
Parents decided following rules for the summer vacation. If the sun is shining or the temperature is above 25 degrees Celsius, kids can have an ice cream. If both conditions are met, kids can also play in the sprinklers in the backyard.
Pen & Paper
Here is a sample dataset for five days of summer vacation:
Date |
Temperature |
Sunshine |
|---|---|---|
July 5th |
23 deg |
Yes |
July 6th |
25 deg |
Yes |
July 7th |
24 deg |
No |
July 8th |
27 deg |
Yes |
July 9th |
26 deg |
No |
Draw a Venn diagram like the one below and place the remaining days in the correct sections of the diagram.
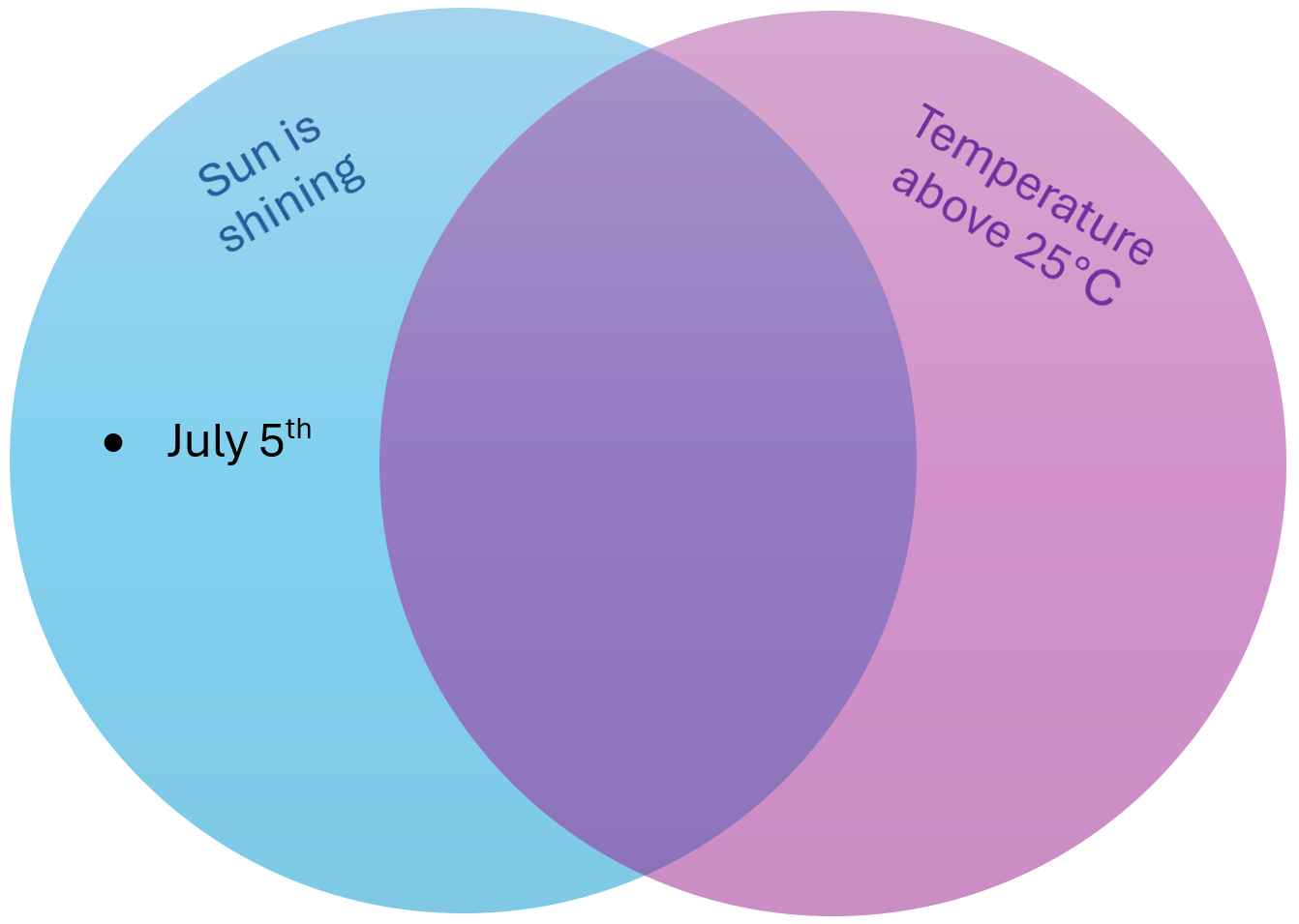
Extend the table with the columns “Temperature OK” and “Sunshine OK”, “Ice Cream” and “Sprinklers” and fill them out with True or False. Here, “Temperature OK” is true if the temperature is above 25 degrees, “Sunshine OK” is true if the sun is shining, “Ice Cream” is true if kids can have an ice cream, and “Sprinklers” is true if kids can play in the sprinklers.
On what days can the kids have an ice cream? On what days can they play in the sprinklers?
Demo
Write a script which given a numeric value temperature and a boolean sunshine computes two boolean variables ice_cream and sprinklers according to the rules above. The code should print the two values. Test your code with all the cases from the Pen & Paper exercise.
Code 3.3: How’s the Weather?#
Write a piece of code that defines a numeric variable temperature and assigns it a value which could be a realistic temperature in degrees Celsius (for example, -8, 2.5, or 26).
Then, write an if statement that prints It is freezing if the temperature is negative. Nothing should be printed if the temperature is zero or positive. Test your code with zero, positive, and negative values for temperature.
Modify your code from the previous exercise by adding an else clause. The code should still print It is freezing for negative temperatures, but it should print It is not freezing for non-negative temperatures.
Modify your code so that it prints:
It is freezingfor temperatures below 0.It is coldfor temperatures between 0 (inclusive) and 15 (inclusive).It is pleasantif the temperatures between 15 (exclusive) and 25 (inclusive).It is hotfor temperatures above 25.
You should achieve this behavior by adding elif clauses.
Test your code with different values of temperature to ensure it works for all cases. At a minimum, test with the values -10, 0, 10, 15, 20, 25, and 30.
Code 3.4: Christmas Presents#
Write code that starts by defining a string variable month and an integer variable day, for example:
month = "May"
day = 24
Write code that prints Let's open presents! if the month is December and the day is the 24th. Otherwise, the code should print No presents today :(. Test your code with different values of month and day including to 13th of December, 24th of December, 26th of December, 4th of May, and 24th of May.
Now, modify your code such that it prints Radio plays 'Last Christmas'. if the month is December. It should still print Let's open presents! on the 24th of December and No presents today :( otherwise. Thus, if the month is December, two messages should be printed: one regarding the music and one regarding the presents. Test your code with the same values of month and day as in the previous exercise.
Code 3.5: Fix Buggy Code#
You asked your friend to write some code for your project. The runs without errors but you are not sure if it works correctly. Your task is to test the code and identify any bugs.
You are welcome to discuss this task with your classmates.
The first piece of code is supposed to find the largest of three numbers. Can you identify the situation where the code produces incorrect results? Can you fix the code?
if x > y and y > z:
largest = x
elif y > z and z > x:
largest = y
else:
largest = z
Hint
What is the value of largest if the values of x, y, and z are 3, 1, and 2, respectively?
The code below should print Weekend only if the day_of_week is equal to either "Saturday" or "Sunday". Test the code. Does it work correctly?
if day_of_week == "Saturday" or "Sunday":
print("Weekend")
else:
print("Work work.")
Hint
Remember that expressions are evaluated from left to right. After evaluating 'Monday' == "Saturday" to False, Python needs to evaluate False or "Sunday". In this expression, or operates between a boolean and a string. How Python does this is an advanced topic not covered in the course. You should just understand that the result is not as desired for the situation at hand. However, you should be able to write the correct condition.
Code 3.6: Ordinal for Digit#
Assume that the variable digit has a value that is a positive digit (i.e., a number 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, or 9). Write a piece of code that stores the string with the ordinal number representation of digit in the variable ordinal. The value of ordinal should be either "1st", "2nd", "3rd", "4th", "5th", "6th", "7th", "8th", or "9th". For example, if digit is 3, then ordinal should be "3rd".
Code 3.7: Special Case#
Consider the following code:
number_of_experiments = 120
number_of_successes = 30
probability_of_success = number_of_successes / number_of_experiments
print(probability_of_success)
If number_of_experiments has the value 0, the division on line 3 will raise a ZeroDivisionError. (Try it!)
Modify the code so that it checks for this case and computes probability_of_success only if number_of_experiments is different from 0. If number_of_experiments is 0, the code should print The probability of success is undefined, since the number of experiments is 0.
Problem Solving#
Problem 3.8: Body Temperature#
Core body temperature is classified as:
Hypothermia: temperature less than or equal to 35 °C.
Normal: temperature greater than 35 °C and less than 37.5 °C.
Hyperthermia: temperature greater than or equal to 37.5 °C and less than 40 °C.
Hyperpyrexia: temperature greater than or equal to 40.0 °C.
Write a piece of code that defines a float variable temperature with a value of your choice, say 37.2. Then, based on the value of temperature, assign a string variable state that can take the values 'hypothermia', 'normal', 'hyperthermia', or 'hyperpyrexia'. Finally, use the print statement:
print("The temperature", temperature, "is", state)
to print the message, as shown below, where 37.2 is the value of temperature:
The temperature 37.2 is normal
Test your code with different values of temperature to make sure it works for all cases. At least, test with values 34.9 (the state should be hypothermia), 35 (also hypothermia), 36.2 (normal), 37.5 (hyperthermia), 37.9 (hyperthermia), 40.0 (hyperpyrexia), and 40.1 (hyperpyrexia). You don’t need to check whether the temperature is physically possible.
Problem 3.9: Valid Class#
Schoolchildren are divided into classes. The class is valid if the total number of children is not less than 20 and not greater than 30. Furthermore, there should be a balance between the number of girls and the number of boys in the class. For the class to be valid, the difference between the sizes of these two groups should not be greater than 5.
Write a piece of code that defines two integer variables number_girls and number_boys. Then, based on the values of these variables, assign a boolean variable is_valid, which is True if the class is valid and False otherwise.
Finally, use the print statement:
print("Class with", number_girls, "girls and", number_boys, "boys is valid:", is_valid)
to print the message as shown below, where number_girls is 18 and number_boys is 11:
Class with 18 girls and 11 boys is valid: False
Test your code with different values to ensure it works as expected. You don’t need to check whether the number of children is positive.
A good way to test the code is to create a table with different values of number_girls and number_boys, along with the expected value of is_valid. For example, the table below shows the expected values for some cases. Make sure your code gives the expected value for all cases in the table.
|
|
expected value of |
comment |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
all fine |
|
|
|
class too large |
|
|
|
class too small |
|
|
|
all fine |
|
|
|
all fine |
|
|
|
too many boys |
|
|
|
multiple conditions unmet |
|
|
|
multiple conditions unmet |
Problem 3.10: Risk of Heart Attack#
Write a piece of code that determines the risk of a person having a heart attack based on the following decision tree:
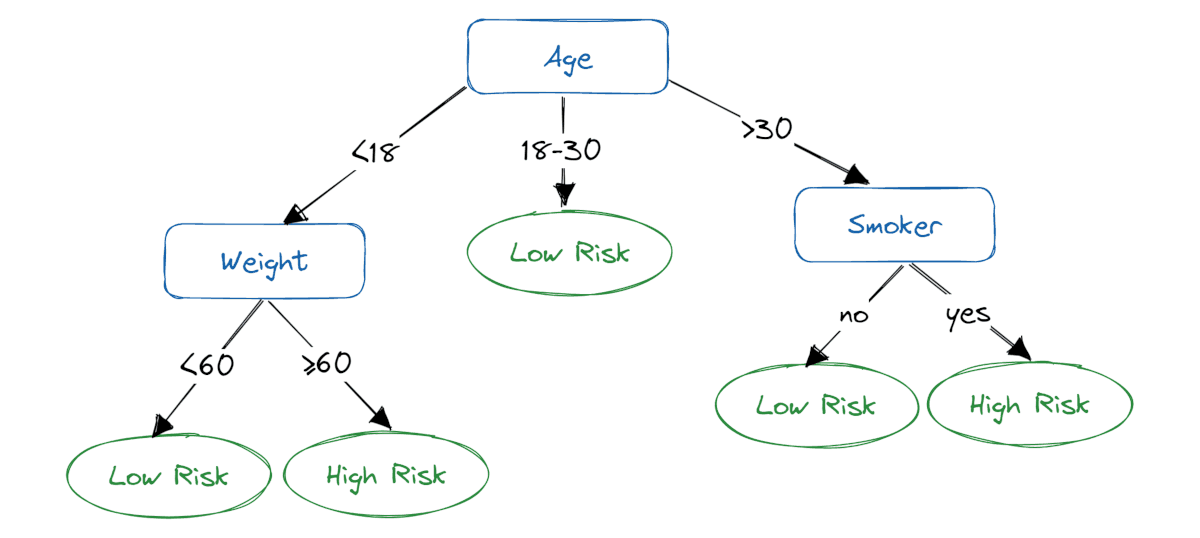
Your code should first define three variables: age (an integer), weight (an integer), and variable is_smoker (a boolean). For example:
age = 45
weight = 80
is_smoker = False
Then, the code should assign a boolean variable high_risk which is True if the risk is high according to the decision tree, and False if the risk is low.
Use a print statement:
print("Age", age, "weight", weight, "smoker", is_smoker, "high risk", high_risk)
to test your code.
Test your code with different values of age, weight, and is_smoker to ensure it works for all cases. At least, try the values from the following table:
|
|
|
expected value of |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Problem 3.11: Triangle Type#
Given three numbers, you want to determine whether they are valid side lengths of a triangle and what type of triangle they form. For this, consider the following image.
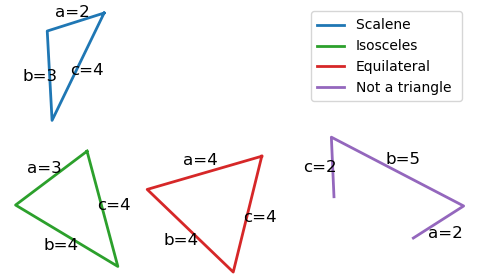
Write a piece of code that defines three float variables a, b, and c, representing the lengths of the sides of a triangle. Based on these numbers, the code should assign a string variable triangle_type which should take one of the following values:
"Invalid lengths"if any of the side lengths is zero or negative."Not a triangle"if the side lengths cannot form a triangle."Scalene"if all side lengths are different."Isosceles"if two side lengths are equal and the third one is different."Equilateral"if all side lengths are equal.
To check whether the side lengths can form a triangle, use the triangle inequality, which states that the sum of the lengths of any two sides must be greater than the length of the remaining side. The inequality must hold for all combinations of two sides.
Test your code with different values of a, b, and c to ensure it works for all cases.
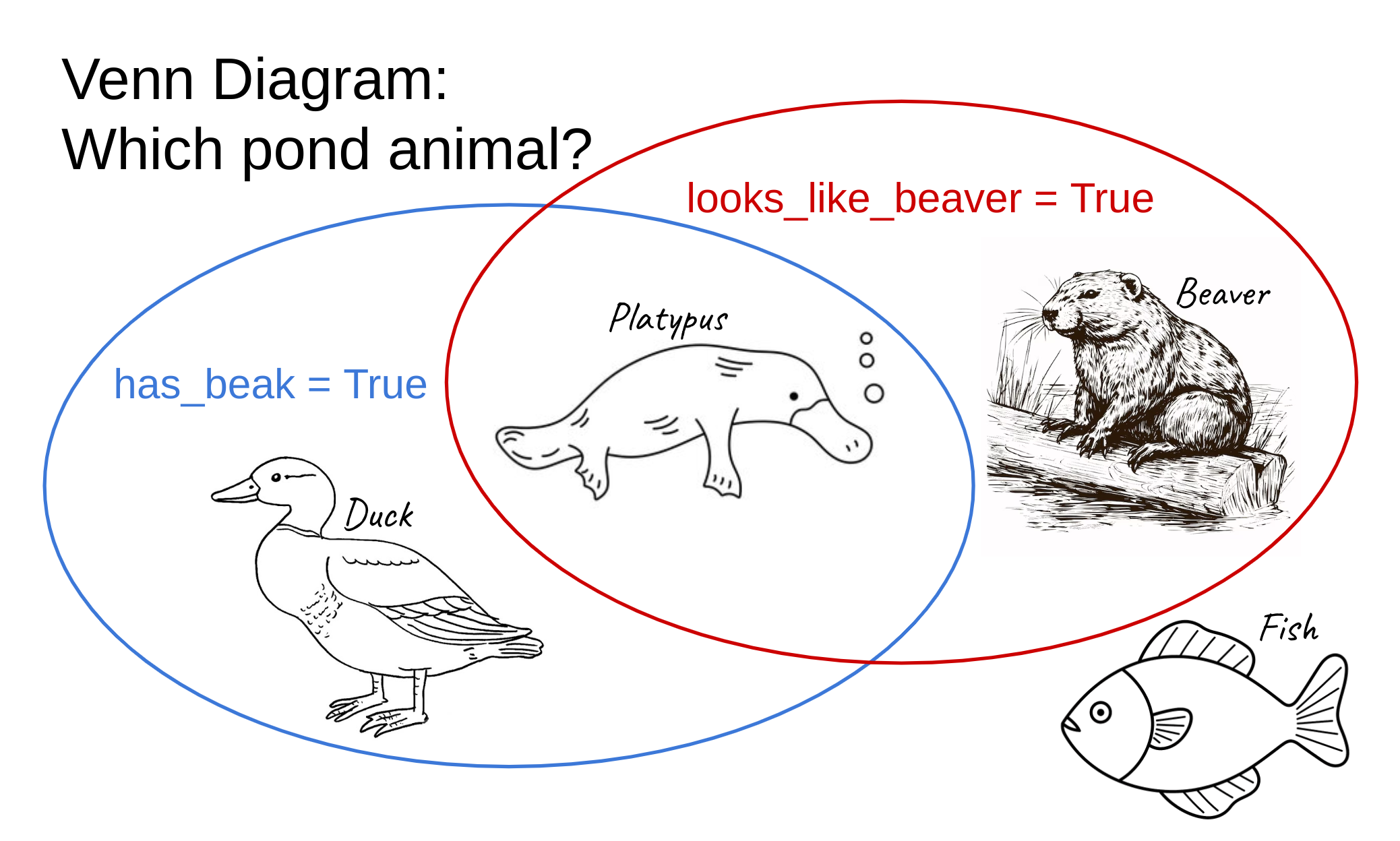
Problem 3.12: Which Pond Animal?#
You are near a pond, and you hear an animal; however you cannot see it. Your programmer friend, who doesn’t know many animals, will help you identify the animal. He tells you the following information:
The variable
looks_like_beaverisTrueif the animal looks like a beaver.The variable
has_beakisTrueif the animal has a beak.
Using this information, you should assign the variable animal to take the string value "duck", "platypus", "beaver", or "fish" according to the Venn diagram below.
Problem 3.13: Battery Status #
A device reports its battery status based on two values: charge_percent (an integer from 0 to 100 giving charge percent) and is_charging (a boolean that is True if the battery is charging, False otherwise). The charging is assumed to be linear and it always takes 180 minutes to go from 0% to 100%. To compute the time left until the battery is fully charged, you can use the formula
Write a piece of code that defines the two variables charge_percent and is_charging. Based on their values, the code should assign a string variable battery_status with the message:
Battery full.when charge_percent is 100 (regardless of charging).Battery empty.when charge_percent is 0 and not charging.Battery status <p>%.when not charging charge percent is neither 0 nor 100.Battery status <p>%. Fully charged in <t> min.when charging and charge percent is smaller than 100.
Here, <p> should be replaced with the value of charge_percent, and <t> should be replaced with the time left until fully charged, rounded to the nearest integer.
Example: If charge_percent is 80 and is_charging is True, the message should be:
Battery status 80%. Fully charged in 36 min.
Problem 3.14: Water Quality #
A monitoring system checks the water quality of a river using two values: ph_level (a float between 0 and 14, representing acidity/basicity) and oxygen_level (a float, in mg/L; 0 means no oxygen present).
The system reports the water status as follows:
Safe for fishwhenph_levelis between 6 and 8 (both values inclusive) andoxygen_levelis larger or equal to 5.Low oxygenwhenoxygen_levelis below 5.Unhealthy pHwhenph_levelis below 6 or above 8, but oxygen is not low.
Task:
Write a piece of code that defines two variables ph_level and oxygen_level.
Based on their values, the code should assign a string variable water_status with the correct message according to the rules above.